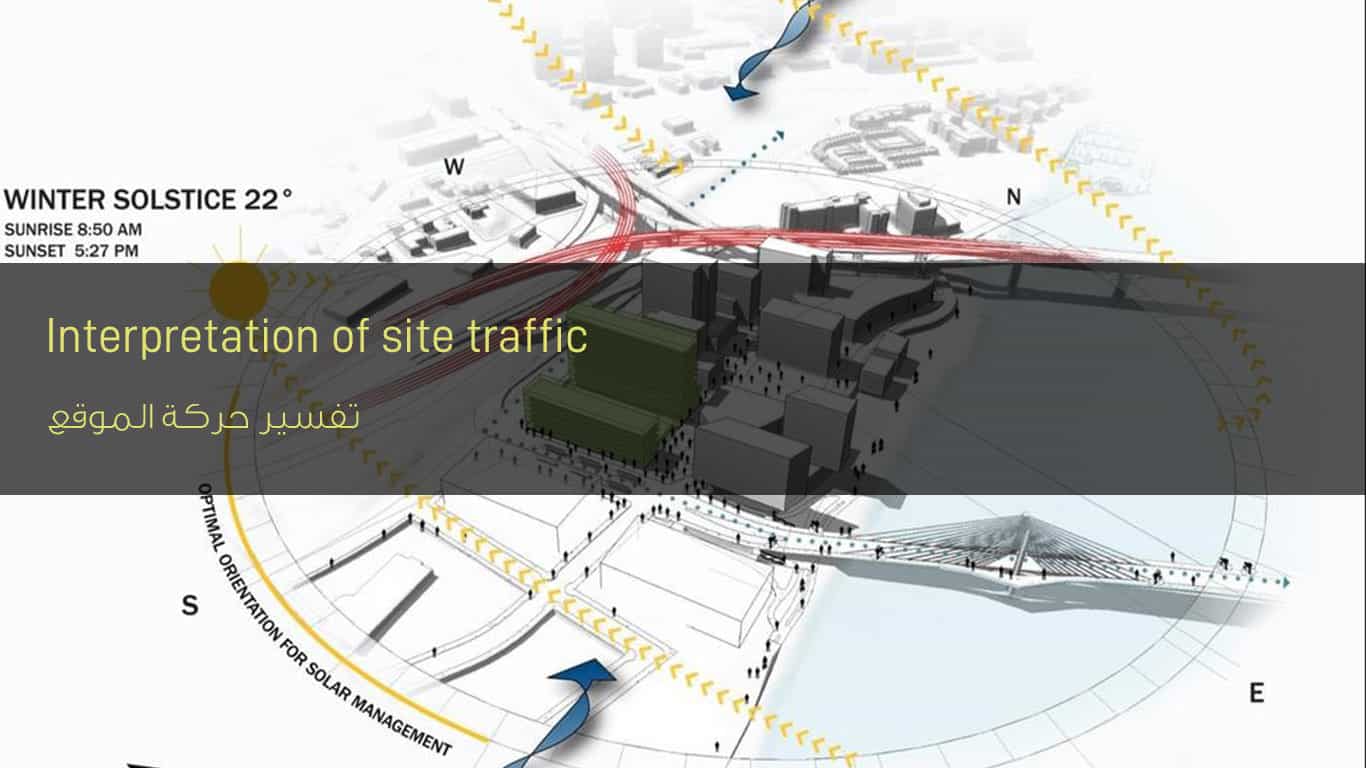
Interpretation of site movement
Interpretation of site movement
Interpretation of site movement – Before design, the site and site elements must be analyzed in detail, including movement, sun, climate, visibility …
Site Analysis Elements
- The wind
- The air moves as a result of the difference in pressure between the high or low regions, due to the difference in the angle of fall of the solar radiation that falls on the surface of the earth.
- The air stream is produced as a result of the presence of currents from the right air under the hot air, as is the case with the transfer of air from land to the sea at night, and then it is transferred from the sea to land during the day.
- Wind direction

Interpretation of site movement – wind direction determination:
Wind direction is determined by:
- Monitor the movement of factory smoke and the movement of trees.
- Follow the windmills as well as wind monitors.
Wind speed :
The wind speed increases with the difference between the pressure in two different places.
Wind intensity:
Wind intensity is measured based on the speed at which objects are pushed.
Wind has different effects, be it at the global level or at the local level.
- The effect on the world level is:
- The difference in the ground distribution of places of atmospheric pressure.
- The constant daily change of temperatures of both the surface of the earth and the sea.
- Earth’s motion around itself.
In order to take advantage of the prevailing air movement, the openings are directed in the northwest direction, in the northern hemisphere, and some openings are directed to the southwest, in the southern hemisphere.
The impact at the local level is:
- Clear differences in atmospheric pressure.
- Roughness or fineness of the grains of the Earth’s surface.
- The rises or depressions on the surface of the earth.
- In Egypt, all elements of a good climate that provides natural comfort are available in relation to the air that passes in the northern part of the country (northwest), so the air is cold and moisture loaded (pleasant and refreshing air), and the northeast winds are less wet and refreshing than the northwest winds and that As a result of its passage in many dry and desert areas.
- As for the winds blowing in the areas of Upper Egypt, it will be hot and dry winds, as it passes through many desert areas.
- In general, for the air to be pleasant and fresh, it must pass over any water surface, whether natural, artificial water, or shaded areas, in order to increase the humidity in the air.
- The analysis of the elements of the site in a way that explains the movement of wind, sun, climate and vision
Architectural methods used to move and cool the air:
This is done by making areas of high pressure from which air moves to areas of low pressure, which results in movement of air currents, whether at the level of the place, city or building.
- At the city level: where the streets and large areas are of low pressure, as a result of the continuous fall of sunlight throughout the day, and whenever the spaces are narrowed, they are of high pressure as a result of the creation of a cold movement of air permeating inside the architectural units.
- At the building level: where the inner and narrow courtyards and vaulted entrances are vertical, are of high pressure and are considered a storehouse of cool and fresh air.
Grabs are used in dry and hot areas in order to obtain the best air currents without the need to direct the building completely to the wind directions and in the event that the wind directions are sometimes not suitable for the angles of the sun fall.
Determinants of good natural ventilation techniques:
- Orientation: Site directions must be studied well, in order to obtain the best ventilation, preferably to adjust directions to the north or the sea side, and the number of openings in the southern facades should be reduced, and if any problems occur in the directions of orientation from the north, such as the presence of a neighbor or others, a separate yard must be made. For ventilation.
- The shape of the ventilation holes, as well as the shape of the building: the height of the openings must be high in order to obtain the highest amount of air, and there must be some opposite openings in the building, in order for one to enter the air and the other for the air to exit, and in the design of the openings it must be an opening The entrance is small and the exit is large, in order for air to penetrate the building.
- Availability of Airlock: The roof is a vertical upper openings in the ceiling, which are placed in the direction of air in order to create air deflection due to the exit of the air in the building’s voids.
- Use of site coordination elements: such as the use of natural elements such as trees, rivers and any surfaces or pools and support them in the direction of wind gusts.
- Designing buildings around the yards: by designing the full and semi-closed enclosed yards.
- The use of shades in ventilation: By designing buildings that are close to and varying in size, large buildings are shaded over small ones.
Air movement changes at the level of residential areas:
Wind direction varies depending on:
- Building heights.
- Distribute the space between the buildings and some of them.
There are two types of air movement:
- Building level movement.
- Movement at the vacuum level.
Also browse: The stages of site analysis