Materials in architecture
Materials in architecture
Materials in Architecture – Throughout history it has allowed the development of new materials and technologies to develop architectural buildings, and also works to develop architecture from a functional and aesthetic point of view, with the emergence of sustainable architecture, the role of materials science in building innovation has become more prominent, where we discover that Architectural materials science and architectural design, as well as their impact on this field.
Texture in architecture
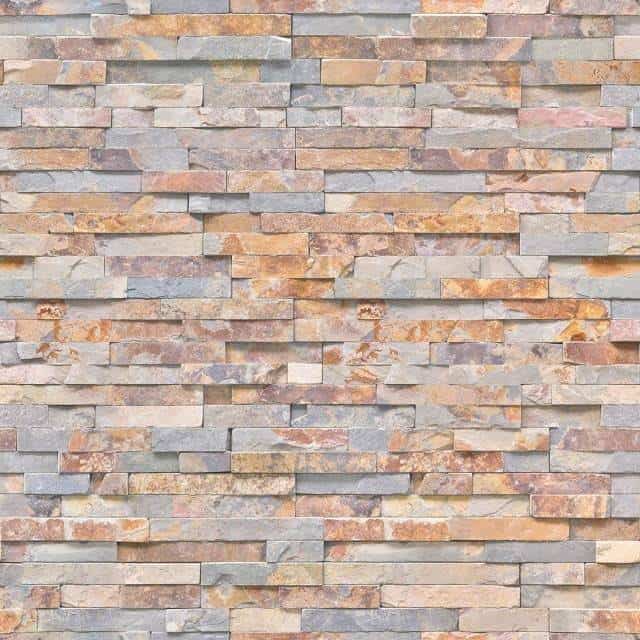
Texture plays a dual role in architecture, as it expresses the quality of the material, and gives a certain quality to light, although one absorbs both traits with the eye simultaneously, the first has tangible, and the second has visual connections.
The specific tactile textures are specific to each material that is used in manufacturing, but we can modify them to produce a variety of expressive qualities for them, and any stone can be used in its natural and irregular condition, or it may be engraved in a rough, smooth, or highly polished material To transfer a set of meanings from strength to purification.
Visible textures are produced by the patterns given for surface illumination by the way materials work for example the vertical or horizontal chisel of a stone, by the method that is used in construction for example in terms of vertical or horizontal ascending or projection and stagnation of brick cycles like all patterns, It creates the texture or visual texture with links for movement, which gives a rhythm to the surface.
Rarely a single fabric is used in construction, but the diversity of materials and treatments usually results in a complex set of textures that must be configured to match the shapes and sizes of architecture in each expressive unit consistent.
Similar topic: Touch and its relationship to architecture
Color in architecture
Since color is a hallmark of all building materials, it is a constant feature of architecture, but building materials are primarily chosen for their structural value, and their colors are not always suitable for expressive requirements and therefore other materials that are frequently chosen for color are added to the surface and these pigments include, which It usually maintains the original surface texture, stone and wood veneer and a variety of manufactured products that completely change the nature of the surface.
But color no matter how it is produced is the most persistent element in architecture where it changes with weathering and staining of materials, as it can be easily changed or removed (like the colored plaster veneer of ancient Greek temples).
Architectural environment
Architecture, unlike most other arts, is often not conceived independently of a particular setting, as design problems go beyond the organization of space and group complexes to include the association of the gross shape with its natural and architectural environment.
Consideration should be given to site layout, which is an essential function of architectural design, the architect aims to create harmony with pre-existing elements in landscape and “city view”.
Decoration in architecture
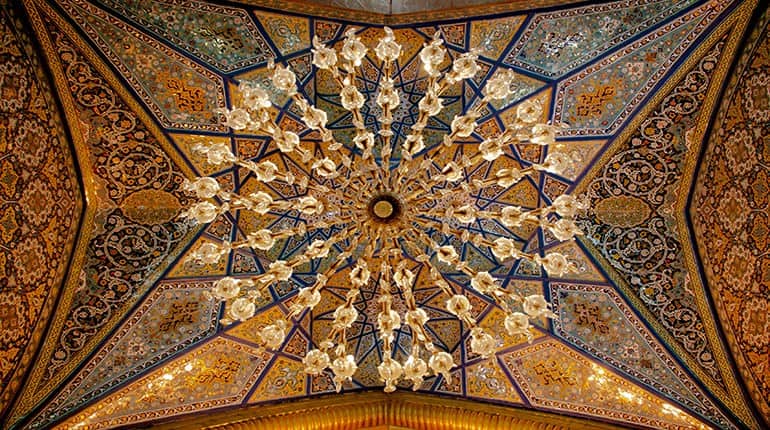

Although it would be difficult to cover in any one definition all concepts, past and present, the decoration in architecture forms an important part of design.
Where we can learn about three basic and somewhat distinct categories: imitation or decoration, which are forms that have certain specific meanings or symbolic importance. There is applied decoration aimed at adding beauty to the external structure and also the organic decoration inherent in a particular function of design or building materials.
Materials in architecture is the method used by the designer and the engineer to implement his ideas. By using these materials, the architect can provoke controversy with distinctive designs that attract attention.







